Computer Abbreviations A to Z
Computer Abbreviations are an integral part of the digital lexicon, simplifying complex technological concepts into concise and standardized terms. Understanding these abbreviations is essential for navigating the vast and dynamic world of computers.
At the core of computing, we encounter the CPU, or Central Processing Unit, often regarded as the brain of the computer, responsible for executing instructions. RAM, or Random Access Memory, provides quick and temporary storage for data actively used by the CPU, while ROM, Read-Only Memory, retains essential instructions even when the computer is powered off.
List of Important Computer Abbreviations
These abbreviations extend to programming languages (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, SQL), file formats (PDF, JPEG, PNG), and interface technologies (USB). In the complex tapestry of computing, these abbreviations serve as linguistic shortcuts, fostering efficient communication and comprehension in the ever-evolving world of technology.
Computer Abbreviation is one of the most frequently asked topics in the Computer Awareness section for various Government exams.
| S. No. | Computer Abbreviation | Full-Form |
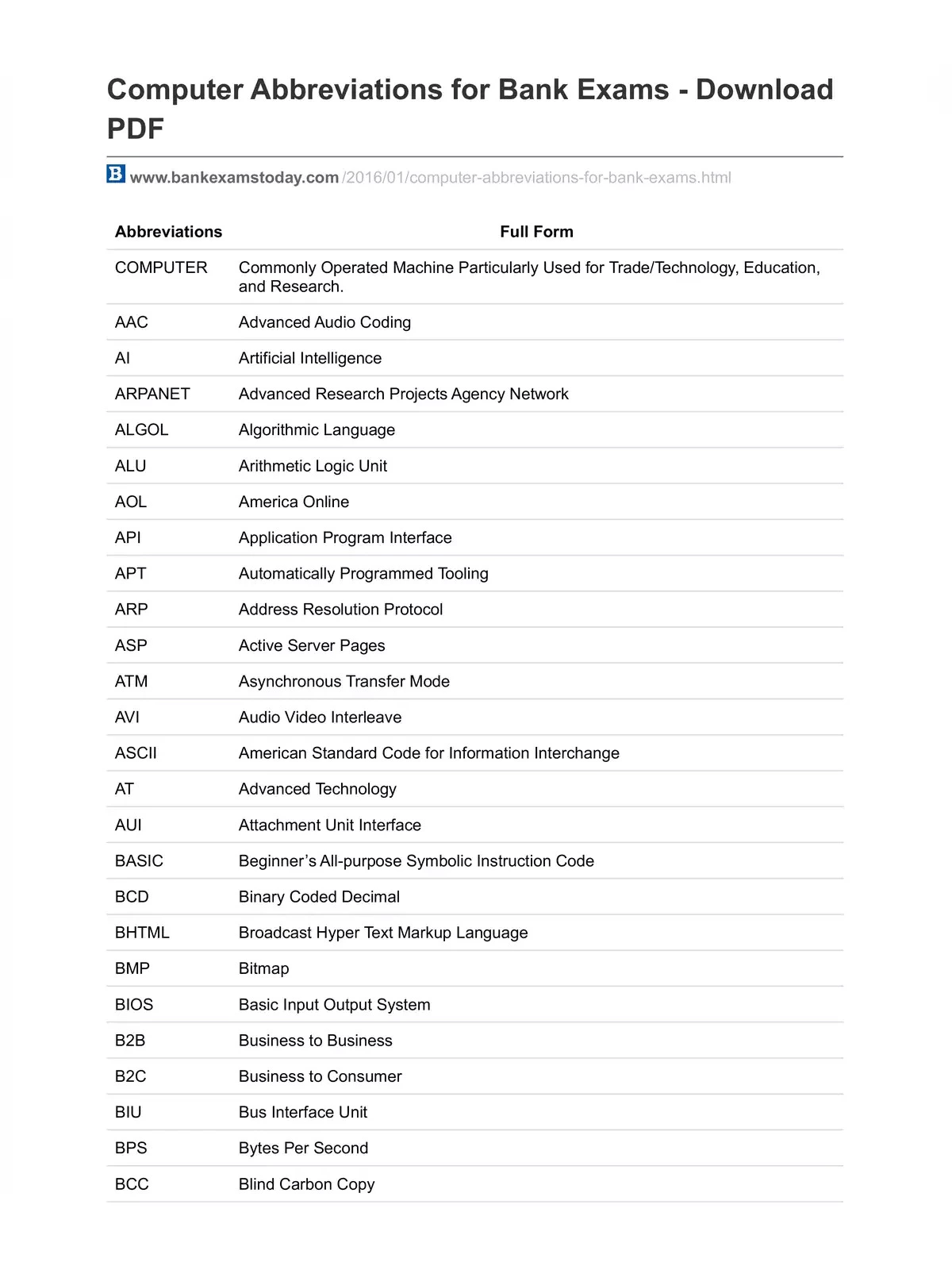
| 1 | AAC | Advanced Audio Coding |
| 2 | ABR | Average Bit Rate |
| 3 | ADSL | Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line |
| 4 | AGP | Advanced Graphics Port |
| 5 | AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| 6 | AIM | AOL Instant Messenger |
| 7 | ALGOL | Algorithmic Language |
| 8 | ALU | Arithmetic Logic Unit |
| 9 | AOL | America Online |
| 10 | AMD | Advanced Micro Devices |
| 11 | API | Application Program Interface |
| 12 | APT | Automatically Programmed Tooling |
| 13 | ARP | Address Resolution Protocol |
| 14 | ARPANET | Advanced Research Projects Agency Network |
| 15 | ARQ | Automatic Repeat Request |
| 16 | AS | Autonomous System |
| 17 | ASCII | American Standard Code for Information Interchange |
| 18 | ASP | Active Server Pages |
| 19 | ASPI | Advanced SCSI Programming Interface |
| 20 | ATA | Advanced Technology Attachment |
| 21 | ATDT | Attention Dial Tone |
| 22 | AUI | Attachment Unit Interface |
| 23 | AUTOEXEC | Autoexec Automatic Execution file |
| 24 | AVI | Audio Video Interleave |
| 25 | BASIC | Beginner’s All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code |
| 26 | BCC | Blind Carbon Copy |
| 27 | BCD | Binary Coded Decimal |
| 28 | BCR | Bar Code Reader |
| 29 | BDSL | Broadband DSL |
| 30 | BEDO | Burst Extended Data Out (RAM) |
| 31 | BGP | Border Gateway Protocol |
| 32 | BHTML | Broadcast Hyper Text Markup Language |
| 33 | BIOS | Basic Input Output System |
| 34 | BIPS | Billion Instruction Per Second |
| 35 | BIU | Bus Interface Unit |
| 36 | BMP | Bitmap |
| 37 | BRD | Blu-Ray Disc |
| 38 | CC | Carbon Copy |
| 39 | CD | Compact Disk |
| 40 | CD-R | Compact Disk – Recordable |
| 41 | CDROM | Compact Disk Read Only Memory |
| 42 | CDRW | Compact Disk Rewritable |
| 43 | CD-WO | Compact Disk – Write Once |
| 44 | CD-XA | Compact Disk – Extended Architecture |
| 45 | CGI-BIN | Common Gateway Interface – Binary (programming for Web forms) |
| 46 | CIS | CompuServe Information Service |
| 47 | CISC | Complex Instructions Set Computers |
| 48 | CMD | Command |
| 49 | CMYK | Cyan-Magenta-Yellow-Black (color model) |
| 50 | CNM | Circulatory Network Mode |
| 51 | COAX | Coaxial Cable (for Ethernet and similar networks) |
| 52 | COBOL | Common Business Oriented Language |
| 53 | COMPUTER | Commonly Operated Machine Particularly Used for Trade/Technology, Education, and Research. |
| 54 | CPI | Clock / Cycle Per Instruction |
| 55 | CPU | Central Processing Unit |
| 56 | CROM | Computerized Range of Motion |
| 57 | CRT | Cathode Ray Tube( standard type computer monitor display |
| 58 | CSLIP | Compressed Serial Line Interface Protocol (Internet) |
| 59 | CSS | Cascading Style Sheets |
| 60 | CTRL | Control (computer keyboard key) |
| 61 | CUI | Character User Interface |
| 62 | DAC | Data Acquisition and Control |
| 63 | DAT | Digital Audio Tape |
| 64 | dB | Decibel |
| 65 | DBMS | Data Base Management System |
| 66 | DDL | Data Definition Language |
| 67 | DHTML | Dynamics Hyper Text Markup Language |
| 68 | DML | Data Manipulation Language |
| 69 | DNS | Domain Name System |
| 70 | DOC | Data Optimizing Computer |
| 71 | Doc | Document |
| 72 | DOS | Disk Operating System |
| 73 | DRAM | Dynamic Random Access Memory |
| 74 | DVD | Digital Video/Versatile Disc |
| 75 | DVDR | Digital Versatile Disk Recordable |
| 76 | DVDRW | Digital Versatile Disk Rewritable |
| 77 | DCE | Data Communications Equipment |
| 78 | DVI | Digital Visual Interface |
| 79 | DVR | Digital Video Recorder |
| 80 | E-Commerce | Electronic Commerce |
| 81 | EDC | Electronic Digital Computer |
| 82 | EDI | Electronic Data Interchange |
| 83 | EDP | Electronic Data Processing |
| 84 | EEPROM | Electronically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory |
| 85 | EFS | Encrypted File System |
| 86 | EIDE | Enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics |
| 87 | Electronic Mail | |
| 88 | EPROM | Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory |
| 89 | EROM | Erasable Read Only Memory |
| 90 | FDD | Floppy Disk Drive |
| 91 | GB | Giga Byte |
| 92 | GDI | Graphical Device Interface |
| 93 | GUI | Graphical User Interface |
| 94 | HD | Hard Disk |
| 95 | HTML | Hyper Text Markup Language |
| 96 | HTTP | Hyper Text Transfer Protocol |
| 97 | I/O | Input/Output (serial and parallel ports) |
| 98 | IC | Integrated Circuit |
| 99 | IMAP | Internet Message Access Protocol |
| 100 | INTEL | Integrated Electronics |
| 101 | IOP | Input Output Processor |
| 102 | IP | Internet Protocol |
| 103 | ISDN | Integrated Services Digital Network |
| 104 | ISP | Internet Service Provider |
| 105 | IVR | Interactive Voice Response |
| 106 | KB | KILOBYTE |
| 107 | Kbps | Kilobits/Kilobytes Per Second |
| 108 | LAN | Local Area Network |
| 109 | LED | Light Emitting Diode |
| 110 | LLL | Low Level Language |
| 111 | LPT | Line Printer |
| 112 | MAC | Media Access Control |
| 113 | MAN | Metropolitan Area Network |
| 114 | MB | Motherboard/ Megabyte |
| 115 | MBASIC | Microsoft BASIC (Microsoft) |
| 116 | MBPS | Megabytes Per Second |
| 117 | Mbps | Megabits Per Second |
| 118 | MICR | Magnetic Ink Character Recognition |
| 119 | MMX | Multimedia Extensions |
| 120 | MODEM | Modulator Demodulator |
| 121 | MSCDEX | Microsoft Compact Disc Extension |
| 122 | MS-DOS | Microsoft – Disk Operating System |
| 123 | NAT | Network Address Translation |
| 124 | NTP | Network Time Protocol |
| 125 | OCR | Optical Character Reader |
| 126 | OMR | Optical Mark Reader |
| 127 | OOP | Object Oriented Programming |
| 128 | OS | Operating System |
| 129 | P2P | Point to Point Protocol |
| 130 | PAN | Personal Area Network |
| 131 | PC | Personal Computer |
| 132 | PCB | Printer Circuit Board |
| 133 | PCI | Peripheral Component Interconnect |
| 134 | PHP | Hypertext Preprocessor |
| 135 | PIXEL | Picture Element |
| 136 | PNG | Portable Network Graphics |
| 137 | PPP | Point to Point Protocol |
| 138 | PRN | Printer |
| 139 | PROM | Programmable Read Only Memory |
| 140 | RAM | Random Access Memory |
| 141 | RARP | Reverse Address Resolution Protocol |
| 142 | RDBMS | Relational Data Base Management System |
| 143 | RIP | Routing Information Protocol |
| 144 | RISC | Reduced Instruction Set Computer |
| 145 | ROM | Read Only Memory |
| 146 | SAM | Software Asset Management |
| 147 | SAN | Storage Area Network |
| 148 | SCSI | Small Computer System Interface |
| 149 | SDRAM | Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory |
| 150 | SFTP | Secure File Transfer Protocol |
| 151 | SGML | Standard Generalized Markup Language |
| 152 | SGRAM | Synchronous Graphics RAM |
| 153 | SIP | Session Initiation Protocol |
| 154 | SIU | Serial Interface Unit |
| 155 | SMTP | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol |
| 156 | SNAP | Sub Network Access Protocol |
| 157 | SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol |
| 158 | SRAM | Static Random Access Memory |
| 159 | SYSOP | System Operator |
| 160 | TCP | Transmission Control Protocol |
| 161 | UI | User Interface |
| 162 | URL | Uniform Resource Locator |
| 163 | USB | Universal Serial Bus |
| 164 | VCD | Video Compact Disk |
| 165 | VDU | Visual Display Unit |
| 166 | VIRUS | Vital Information Resource Under Siege |
| 167 | VRAM | Video Random Access Memory |
| 169 | VxD | Virtual Extended Driver |
| 170 | WAN | Wide Area Network |
| 171 | WAP | Wireless Application Protocol |
| 172 | WBMP | Wireless Bitmap Image |
| 173 | WIFI | Wireless fidelity |
| 174 | WLAN | Wireless Local Area Network |
| 175 | WML | Wireless Markup Language |
| 176 | WWW | World Wide Web |
| 178 | XGA | Extended Graphics Array |
| 179 | XHTML | Extensible Hyper Text Markup Language |
| 180 | XMF | Extensible Music File |
| 181 | XML | Extensible Markup Language |
| 182 | XMS | Extended Memory Specification |
| 183 | FORTRAN | Formula Translation |
You can download the Computer Abbreviations in PDF format using the link given below.